 |
|
| What We Do | What We Have Done |
Case Studies | Why LimNorris? | Company Info | FAQ | Contact Us |
The Scenario: Uncontrolled proliferation of servers
To satisfy specific business needs, a Mainframe-centric IT Department began deploying solutions on Intel and UNIX platforms. The assessment for the Year 2000 project unveiled that they had over 100 servers worldwide and some of them ran critical business systems. The IT Department had mature processes and tools to support Mainframe availability. None existed for Intel and UNIX servers and Y2K was only seven months away.
The Challenge: Mainframe-level availability
Define support processes and tools to ensure availability for Intel and UNIX servers was at least equivalent to the Mainframe's target availability of 99.7%. Deploy the processes and tools before November 1999 for Y2K.
The Approach: Assess, plan, implement, and improve
We assessed the current state by manually tracking Intel/UNIX outages, interviewing support personnel, and reviewing Mainframe processes and tools. Next we investigated system management tools and selected Tivoli IT Director. We developed an incident escalation process that took advantage of Tivoli's automated notifications and developed a capacity planning process modeled after the Mainframe process. Our objective was to pro actively identify and correct problems before an outage occurred. We incrementally deployed the tools and process to minimize implementation risk. During implementation, we reviewed actual incidents and used them to refine and improve the processes and tools.
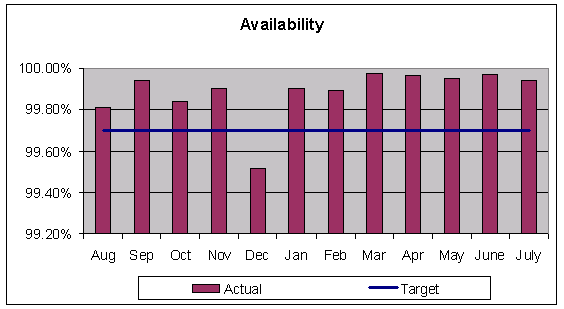
The Result: Exceeded Mainframe-level availability
Processes and tools were deployed by November 1999 and were used during the Y2K transition. Availability of Intel/UNIX servers in the first quarter of 2000 was 99.9%, exceeding the target of 99.7%. Availability continued to improve and reached 99.96% in 2001.
|
Copyright 2002 Lim, Norris & Associates, Inc. All rights reserved.
|
|||||||||||||||||